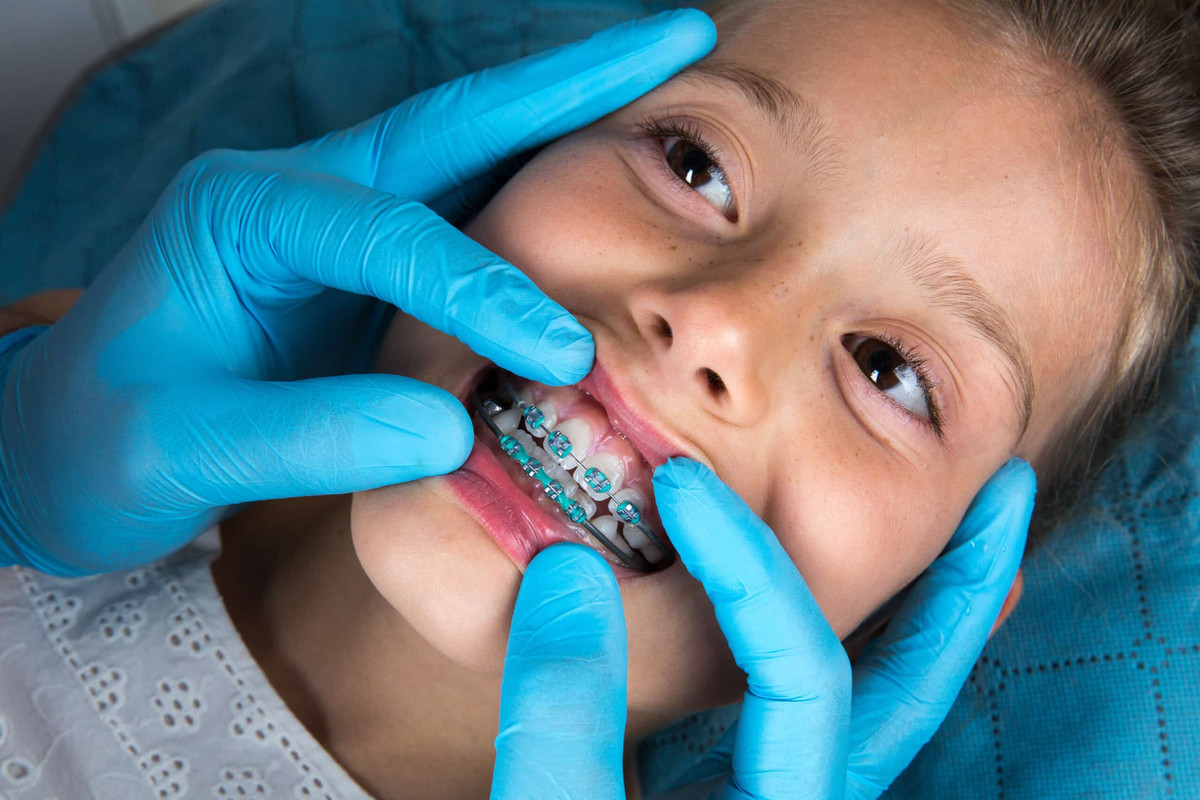
Orthodontic treatments for children are designed to correct misaligned teeth and jaws, improving both function and appearance. Early intervention can be beneficial in addressing issues before they become more complex. Here’s an overview of common orthodontic treatments for children:
**1. Early Intervention (Phase I Treatment):
- Purpose: Early intervention aims to address developing issues while a child’s teeth and jaws are still growing. This can prevent more serious problems from developing later.
- Timing: Typically recommended between ages 7 and 9, when the child’s permanent teeth are starting to come in.
- Common Treatments: May include space maintainers, palatal expanders, or partial braces to address issues like crowding, crossbites, or bite problems.
**2. Braces:
- Traditional Braces: Metal brackets and wires that gradually move teeth into proper alignment. They are effective for a wide range of orthodontic issues and are often used after the growth spurt to correct alignment.
- Ceramic Braces: Similar to traditional braces but made from clear or tooth-colored materials, making them less noticeable.
- Self-Ligating Braces: Braces that use a special clip instead of elastic bands to hold the wire in place, reducing friction and potentially shortening treatment time.
**3. Clear Aligners:
- Invisalign: A series of custom-made clear plastic trays that gradually move teeth into position. These are removable and less noticeable than traditional braces.
- Benefits: Clear aligners are a popular choice for older children and teens who may prefer a less visible option.
**4. Retainers:
- Purpose: Retainers are used after braces or aligners to maintain the new position of the teeth and prevent them from shifting back.
- Types: Fixed retainers (bonded behind the teeth) and removable retainers (plastic trays) are common.
**5. Space Maintainers:
- Purpose: These devices are used to keep space open for permanent teeth when a primary tooth is lost prematurely.
- Types: Band-and-loop, crown-and-loop, and distal shoe maintainers are common types.
**6. Palatal Expanders:
- Purpose: Used to widen the upper jaw if it is too narrow. This creates more space for teeth and improves bite alignment.
- Types: Fixed expanders that are adjusted periodically or removable expanders that can be adjusted by the child’s parent.
**7. Functional Appliances:
- Purpose: Used to correct bite issues or jaw discrepancies. They work by influencing the growth and development of the jaw and teeth.
- Examples: Herbst appliances and twin blocks.
**8. Monitoring and Follow-Up:
- Regular Check-Ups: Frequent visits to the orthodontist are necessary to monitor progress and make any needed adjustments.
- Adjustments: Periodic adjustments to braces or aligners are required to ensure proper movement and alignment of teeth.
**9. Post-Treatment Care:
- Retention Phase: After orthodontic treatment, children will typically need to wear retainers to maintain their teeth in their new positions.
- Ongoing Care: Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential to ensure the long-term success of orthodontic treatment.
Early evaluation by an orthodontist can help determine the best course of action and ensure that any issues are addressed in a timely manner. If you’re considering orthodontic treatment for your child, consulting with a qualified orthodontist will provide personalized recommendations based on your child’s specific needs.